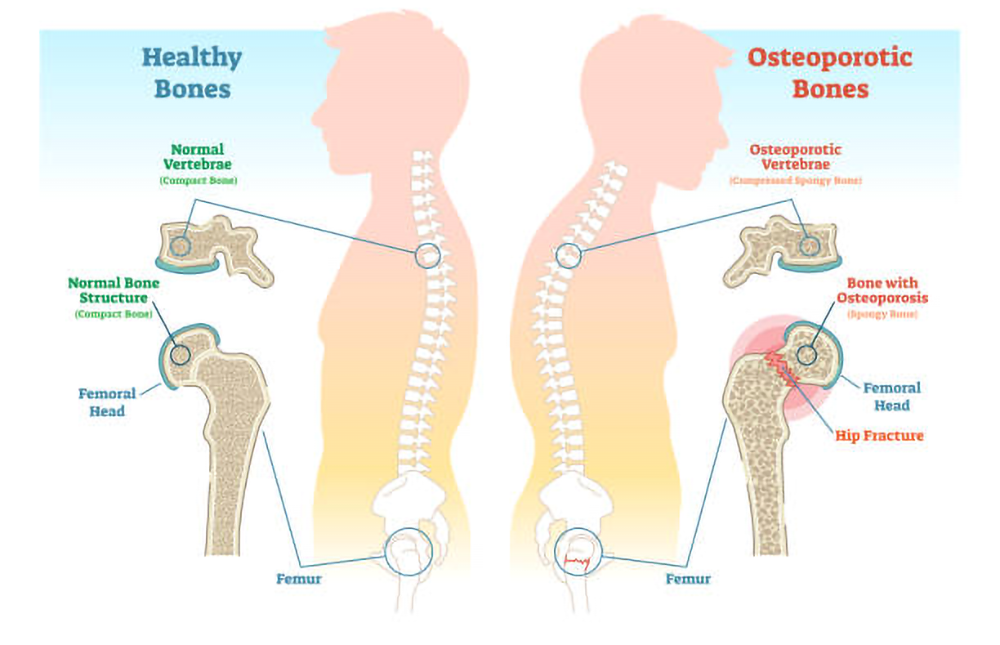
Osteoporosis
A lack of bone density and a higher probability of fractures are the two main features of the prevalent skeletal condition osteoporosis. Due to its asymptomatic nature up until a fracture, it is frequently referred to as the "silent disease" and affects millions of people worldwide, mostly women.
Causes of Osteoporosis
The primary cause is an imbalance between bone formation and bone resorption, resulting in a gradual loss of bone density over time. Factors that can increase the risk of developing osteoporosis include:
- Aging
- Genetics
- Hormonal Imbalances
- Nutritional Deficiencies
- Sedentary Lifestyle
- Medications and Medical Conditions
The natural aging process is a significant risk factor for osteoporosis. As individuals grow older, the rate of bone formation decreases, while bone resorption accelerates. This imbalance leads to a gradual loss of bone density over time.
The probability of getting affected by osteoporosis in an individual can be determined by genetic factors. Bone density, bone shape, and bone turnover rates can be influenced by genetic and hereditary factors. A higher possibility of having osteoporosis appears in those with a family heritage of the disorder.
Osteoporosis risk can be raised by certain medical diseases and hormonal abnormalities that cause bone loss. The delicate balance between bone creation and resorption can be upset by conditions including hyperthyroidism, hypogonadism, and Cushing's disease, which can result in bone loss. Bone health can also be adversely affected by chronic inflammation, which manifests itself in diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus.
Nutrition is essential for maintaining bone health. The development of osteoporosis can be accelerated by inadequate consumption of vital nutrients, which can weaken bones. Inadequate calcium consumption can result in decreased bone density because calcium is a key component of bone tissue. Vitamin D, Magnesium, vitamin K, and protein are a few more nutrients that are crucial for keeping strong bones.
Exercises involving lifting heavy objects and physical activity are beneficial for bone health. Regular physical activity, including jogging, weightlifting, dancing, or walking, stimulates the restructuring of bones and assists in retaining bone density. Muscle deterioration, unstable balance, and reduced bone mass are all effects of a sedentary lifestyle and insufficient exercise. Osteoporosis is more likely to occur in people who refrain from engaging in physical activities.
An elevated risk of osteoporosis has been linked to a number of drugs and medical procedures. Medication-induced osteoporosis is frequently brought on by prolonged usage of corticosteroids. These drugs may prevent the restructuring of bones leading to the breaking down of bones and decreased bone production. Bone health may also be affected by chemotherapy and hormonal cancer treatments.
Prevalent Symptoms of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis often remains asymptomatic until a fracture occurs. However, some individuals may experience the following signs.
- Bone Fractures
- Back Pain
- Fragility Fractures
- Tooth Loss and Gum Problems
Fractures are the most common and significant symptom of osteoporosis. Individuals with weakened bones are more susceptible to fractures, which can occur from seemingly minor incidents such as a fall or even simple everyday activities. The most common fracture sites related to osteoporosis include the spine, hips, wrists, and ribs. These fractures can cause significant pain, limited mobility, and disability.
Back pain is a prevalent symptom experienced by individuals with osteoporosis. It can be persistent, dull, or sharp in nature, and is often a result of fractures in the vertebrae. Vertebral compression fractures can lead to severe back pain that worsens with movement, sneezing, or coughing. The pain can also radiate to the sides of the body.
The bones become more fracture-prone as a result of osteoporosis. Fragility fractures are those that take place in weakened bones by a slight trauma or stress. In people with osteoporosis, a simple fall, lifting a large object, or simply leaning over can result in fractures. Hip, wrist, and rib fractures are particularly frequent.
Osteoporosis can also harm the jawbone, causing tooth loss and gum issues. Gum recession, tooth mobility, and an elevated risk of dental problems can be caused by jawbone thinning. Osteoporosis patients may lose teeth or discover that their dentures no longer fit properly as a result of changes in their bone structure.
Recognizing the symptoms of osteoporosis is crucial for early detection, proper diagnosis, and timely intervention. Hence, it is advised to you to consult your doctor or book an appointment with a healthcare professional through PrimeMedic, if you start to notice any of the above-mentioned symptoms at any age, in order to get yourself treated timely.